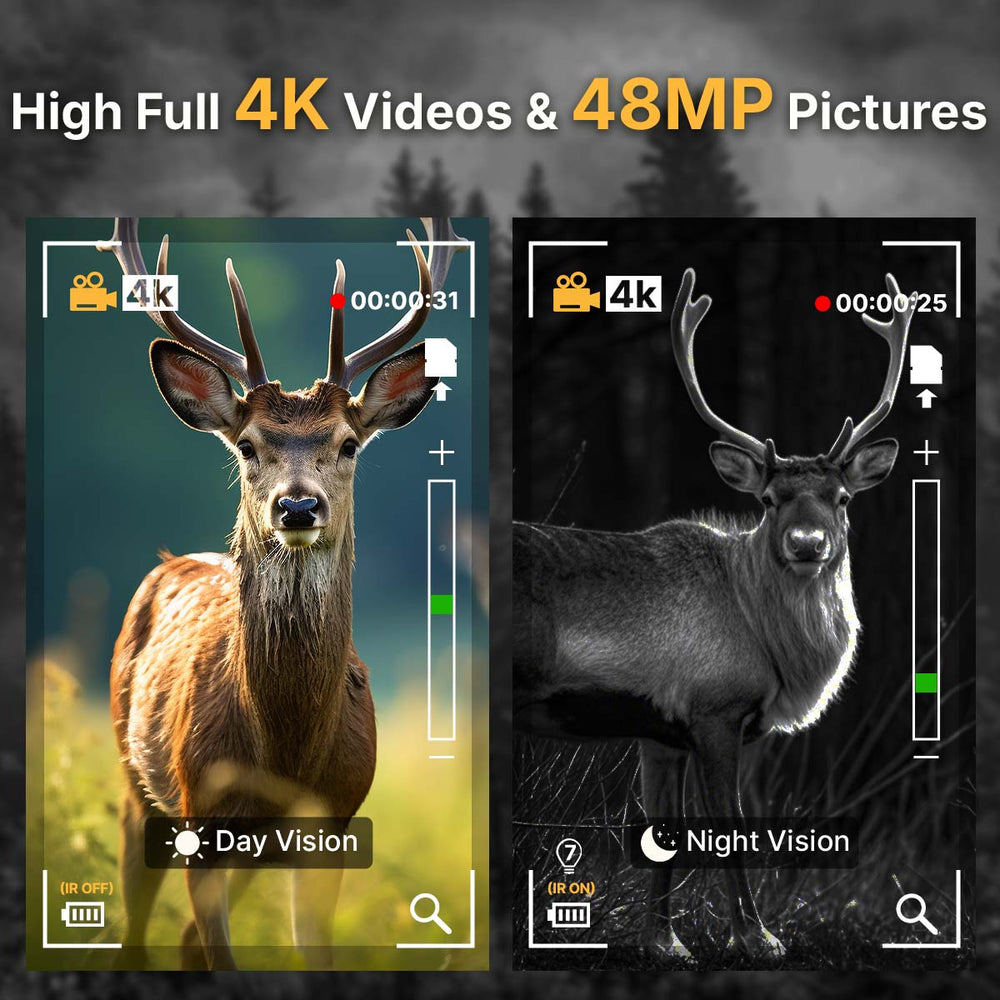
Which is Better, Night Vision Goggles or Infrared Goggles?
In low-light or no-light environments, specialized optical devices like infrared goggles and night-vision goggles (NVGs) are indispensable. However, confusion often arises about their functionalities and use cases. This article explores the differences between infrared goggles and night-vision goggles, supported by technical data, real-world applications, and expert insights.
1. What Are Infrared Goggles?
Infrared goggles (or thermal imaging goggles) detect heat signatures emitted by objects, living beings, or machinery. They operate by capturing infrared radiation (wavelengths: 700 nm–1 mm) invisible to the human eye.
How Do Infrared Goggles Work?
Thermal Sensors: Convert infrared radiation into electrical signals.
Image Processor: Creates a visual map based on temperature differences (warmer objects appear brighter).
Display: Renders the thermal image in grayscale or color palettes (e.g., black-hot/white-hot).
Key Features:
Operate in total darkness and through obstructions (smoke, fog).
Detect temperature differences as small as 0.01°C (advanced models).
No reliance on ambient light.
Applications:
Military: Detecting hidden enemies or IEDs.
Search and Rescue: Locating missing persons in dense forests.
Industrial: Identifying overheating machinery.
2. What Are Night-Vision Goggles?
Night-vision goggles (NVGs) amplify existing light to help the user see in near-total darkness. This includes light from the moon, stars, or infrared light sources invisible to the human eye. NVGs have been widely used since World War II and have evolved through multiple generations.

How Night Vision Works:
Night-vision technology relies on image intensification. Photons (light particles) enter the lens, strike a photocathode, and are converted into electrons. These electrons are then multiplied via a microchannel plate and converted back into visible light on a phosphor screen.
Generations of Night Vision Goggles:
Gen 1: Basic light amplification, affordable but limited range and clarity
Gen 2: Improved resolution and low-light performance
Gen 3: Military-grade, high sensitivity, clear image in near-total darkness
Gen 4 (or Gen 3+ in some classifications): Auto-gated for high-dynamic light environments
Key Features:
Requires minimal ambient light (fails in pitch darkness).
Produces monochromatic images (typically green).
Lightweight and widely used in tactical operations.

Applications:
Military: Navigation and combat in low-light conditions.
Wildlife Observation: Studying nocturnal animals.
Law Enforcement: Surveillance and suspect tracking.
3. Key Differences Between Infrared and Night-Vision Goggles
4. How to Choose Between Infrared and Night-Vision Goggles
Ask Yourself These Questions:
Q: Do I need to operate in zero light?
Go with infrared goggles.
Q: Am I tracking warm-blooded animals or humans?
Infrared is more effective.
Q: Do I need detailed imagery?
Night-vision goggles provide better clarity for shapes and movement.
Q: What's my budget?
Night-vision goggles are generally more affordable.
Best for Beginners:
Best for Professionals:
5. Pros and Cons
Pros
Affordable
Lightweight
Real-time performance
Better identification of shapes and objects in ambient light
Cons
Requires light source
Poor performance in total darkness or smoke
Limited through-glass visibility
Pros
Operates in total darkness
Detects heat signatures
Works in obscured conditions
Cons
More expensive
Cannot identify fine details (e.g., faces)
Heavier and bulkier
what is the recommendation for night vision goggles

Which Is Better: Night Vision or Infrared?
The answer to whether night vision or infrared is better depends on the context in which it is used:
Choose night vision if you need detailed visual identification in environments with some ambient light and want a more affordable solution.
Choose infrared if you must operate in zero-light conditions or through visual obstructions like fog, smoke, or foliage, and you're tracking heat-emitting targets.
Search
Popular Posts
Recent Posts

Nov 28, 2024
Troubleshooting Common Trail Camera Issues
Jan 10, 2025
Why Does My Trail Camera Stop Working at Night?